Eddy’s HR Mavericks Encyclopedia
The world's largest free encyclopedia of HR, with 700+ HR articles and podcasts.
Created by Eddy and our HR Mavericks community.
Organizational Development (OD)
As a business owner or executive leader, how you handle and manage change is critical to your organization’s success. Read on to understand why organizational development is important for your organization's ability to achieve its goals and objectives.
What Is Organizational Development (OD)?
Organizational development (OD) refers to the process of improving the effectiveness of an organization through planned, systematic and collaborative interventions. OD aims to enhance an organization's ability to achieve its goals and objectives by improving its internal processes, systems and structures, as well as the skills, knowledge and behaviors of its employees.
Organizational Development and Human Resources
Are you wondering how OD and HR are different? Here are some ways in which they are related and different:
- Focus. HR focuses on the management of personnel-related functions, such as recruitment, employee relations, compensation, benefits and performance management. On the other hand, OD focuses on the broader aspects of organizational culture, systems, processes and structures that impact employee behavior and performance.
- Approach. HR is often more transactional and reactive, dealing with day-to-day issues and responding to employee needs as they arise. OD takes a more proactive and strategic approach, anticipating and planning for future challenges and opportunities.
- Goals. The primary goal of HR is to ensure that the organization has the right people in the right roles with the right skills, and that they are fairly treated and compensated. OD's goal is to improve organizational effectiveness and performance by enhancing employee engagement, collaboration and innovation.
- Tools and techniques. HR uses a variety of tools and techniques such as job analysis, performance reviews, and training and development programs to manage personnel-related functions. OD uses a range of tools and techniques such as surveys, focus groups and interventions to diagnose and address organizational issues.
The Importance of Organizational Development
Organizational development is important because it helps organizations improve their effectiveness and performance by enhancing their ability to adapt to change, innovate and grow. OD focuses on improving the organization's systems, processes and culture to create a more productive and engaged workforce that is better equipped to achieve the organization's goals. Here are some specific reasons why organizational development is important:
- Increased adaptability. Organizations that embrace OD are better equipped to adapt to changes in the external environment, such as changes in technology, competition or regulations. By focusing on continuous improvement and innovation, OD helps organizations become more flexible and responsive to changing circumstances.
- Improved productivity. OD can help organizations streamline their processes, eliminate waste and improve efficiency. This can result in higher productivity and lower costs, which can enhance the organization's competitiveness.
- Better employee engagement. OD can help create a more engaged and motivated workforce by improving communication, collaboration and employee involvement. This can result in higher employee satisfaction, reduced turnover and increased commitment to the organization's goals.
- Enhanced leadership and management skills. OD can help develop leadership and management skills within the organization by providing training and development programs that improve communication, coaching and performance management.
- Improved organizational culture. OD can help create a positive organizational culture that supports employee well-being, diversity, and inclusion. This can result in higher morale, greater innovation and better decision-making.
Principles of Organizational Development
The principles of organizational development emphasize a holistic and collaborative approach to improving organizational effectiveness. They recognize the importance of continuous learning and improvement in today's rapidly changing business environment. Here are some key principles of organizational development:
Systemic Perspective
OD views organizations as complex systems made up of interrelated parts rather than a collection of individuals. This perspective recognizes that changes in one part of the organization can affect the entire system.
Participative Approach
OD involves active participation and collaboration from all members of the organization, including leaders, managers, employees and stakeholders. This approach values diversity of perspectives and promotes inclusion.
Continuous Improvement
Organizational development is an ongoing process of continuous learning, growth and improvement. This involves regularly assessing and evaluating the organization's performance and making adjustments as needed.
Human Focus
OD recognizes that organizations are made up of people, and therefore emphasizes the importance of understanding and supporting the human aspects of the organization, such as employee engagement, motivation and well-being.
Data-Driven Decision Making
Organizational development uses data and evidence to inform decision making and measure the impact of interventions. This involves collecting and analyzing data on organizational performance, employee feedback and other relevant metrics.
Collaborative Problem Solving
OD encourages collaborative problem solving and decision making. This involves bringing together diverse perspectives and expertise to address complex challenges and find innovative solutions.
Systems Thinking
Organizational development recognizes that organizations are part of larger systems, such as the economy, society and the environment. This involves considering the broader impact of organizational decisions and actions and seeking to create sustainable and responsible organizations.
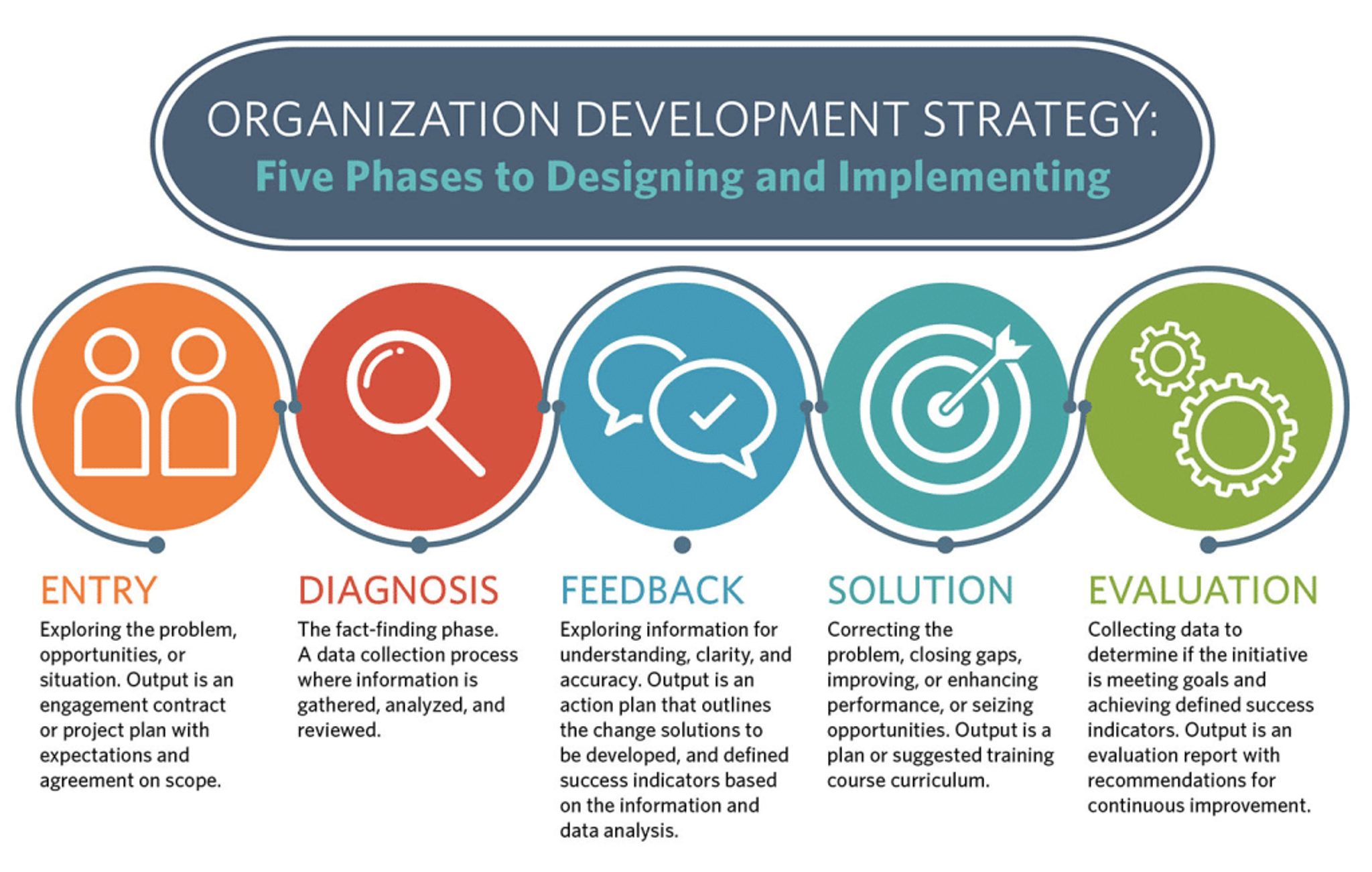
The 5 Stages of Organizational Development
The stages of organizational development can vary depending on the model used, and it's important to note that these stages may not occur in a linear fashion. Organizations may revisit earlier stages as they continue to evolve and grow. Here are some commonly recognized stages:
Stage 1: Entry
The first phase is to enter and diagnose the current state of the organization. This involves identifying the strengths, weaknesses, opportunities and threats of the organization. The diagnosis can be done through surveys, interviews, focus groups and other methods of data collection.
Stage 2: Diagnosis
The second phase is to develop a plan for change based on the diagnosis. This includes setting goals, identifying areas for improvement and selecting appropriate interventions. The plan should be developed collaboratively with key stakeholders in the organization.
Stage 3: Feedback
The third phase is to implement the interventions identified in the planning phase. This will include providing feedback and may also include training, coaching, process redesign, culture change, etc. It is important to involve employees in the implementation process to ensure buy-in and ownership of the changes.
Stage 4: Solution
The fourth phase is to correct the concerns, close the gaps, improve the process and performance and then evaluate the effectiveness of the interventions. This involves measuring the impact of the changes on the organization and its stakeholders. The evaluation should be conducted using both qualitative and quantitative methods and should be ongoing to ensure continuous improvement.
Stage 5: Evaluation
The fifth and final phase is to institutionalize the changes into the organization's culture and processes. This involves embedding the changes into the organization's systems and structures to ensure they are sustainable and become part of the organization's way of doing things. Once implemented, collect data to analyze the effectiveness of the strategies implemented to understand if you are meeting your defined success indicators.
Organizational Development Techniques and Tools
OD techniques and tools improve the effectiveness and efficiency of an organization. There are several techniques and tools that can be used in organizational development. Some of these include:
SWOT Analysis
SWOT (strengths, weaknesses, opportunities, and threats) analysis is a tool that helps organizations identify their internal strengths and weaknesses and external opportunities and threats.
Change Management
Change management is the process of managing organizational change. It involves planning, implementing and monitoring changes to ensure that they are effective.
Team Building
Team building is the process of creating a cohesive team that works together effectively. This can involve team-building activities, training and development.
Process Improvement
Process improvement involves identifying and eliminating inefficiencies in organizational processes to improve efficiency and productivity.
Performance Management
Performance management is the process of setting goals, monitoring progress and providing feedback to employees to improve their performance.
Coaching and Mentoring
Coaching and mentoring are techniques used to develop the skills and knowledge of employees. This can involve one-on-one coaching or group mentoring sessions.
Employee Engagement
Employee engagement involves creating a work environment that fosters employee motivation, commitment and productivity.
Strategic Planning
Strategic planning is the process of defining an organization's goals and objectives and developing a plan to achieve them.
Employee Surveys
Employee surveys are used to gather feedback from employees on various aspects of the organization, such as job satisfaction, communication and leadership.
Training and Development
Training and development programs are used to develop the skills and knowledge of employees. This can include on-the-job training, workshops and seminars.
Topics

Katie Potter, MAIOP
Katie is an executive People & Talent leader with strong demonstration of building and scaling HR teams from startups to corporate teams. She has experience in building strong, globally focused culture & inclusion across remote, hybrid and onsite teams with a strong passion for people, engagement, & talent development.
Frequently asked questions
Other Related Terms
Eddy’s HR Mavericks Encyclopedia
Organizational Development (OD)
As a business owner or executive leader, how you handle and manage change is critical to your organization’s success. Read on to understand why organizational development is important for your organization's ability to achieve its goals and objectives.
What Is Organizational Development (OD)?
Organizational development (OD) refers to the process of improving the effectiveness of an organization through planned, systematic and collaborative interventions. OD aims to enhance an organization's ability to achieve its goals and objectives by improving its internal processes, systems and structures, as well as the skills, knowledge and behaviors of its employees.
Organizational Development and Human Resources
Are you wondering how OD and HR are different? Here are some ways in which they are related and different:
- Focus. HR focuses on the management of personnel-related functions, such as recruitment, employee relations, compensation, benefits and performance management. On the other hand, OD focuses on the broader aspects of organizational culture, systems, processes and structures that impact employee behavior and performance.
- Approach. HR is often more transactional and reactive, dealing with day-to-day issues and responding to employee needs as they arise. OD takes a more proactive and strategic approach, anticipating and planning for future challenges and opportunities.
- Goals. The primary goal of HR is to ensure that the organization has the right people in the right roles with the right skills, and that they are fairly treated and compensated. OD's goal is to improve organizational effectiveness and performance by enhancing employee engagement, collaboration and innovation.
- Tools and techniques. HR uses a variety of tools and techniques such as job analysis, performance reviews, and training and development programs to manage personnel-related functions. OD uses a range of tools and techniques such as surveys, focus groups and interventions to diagnose and address organizational issues.
The Importance of Organizational Development
Organizational development is important because it helps organizations improve their effectiveness and performance by enhancing their ability to adapt to change, innovate and grow. OD focuses on improving the organization's systems, processes and culture to create a more productive and engaged workforce that is better equipped to achieve the organization's goals. Here are some specific reasons why organizational development is important:
- Increased adaptability. Organizations that embrace OD are better equipped to adapt to changes in the external environment, such as changes in technology, competition or regulations. By focusing on continuous improvement and innovation, OD helps organizations become more flexible and responsive to changing circumstances.
- Improved productivity. OD can help organizations streamline their processes, eliminate waste and improve efficiency. This can result in higher productivity and lower costs, which can enhance the organization's competitiveness.
- Better employee engagement. OD can help create a more engaged and motivated workforce by improving communication, collaboration and employee involvement. This can result in higher employee satisfaction, reduced turnover and increased commitment to the organization's goals.
- Enhanced leadership and management skills. OD can help develop leadership and management skills within the organization by providing training and development programs that improve communication, coaching and performance management.
- Improved organizational culture. OD can help create a positive organizational culture that supports employee well-being, diversity, and inclusion. This can result in higher morale, greater innovation and better decision-making.
Principles of Organizational Development
The principles of organizational development emphasize a holistic and collaborative approach to improving organizational effectiveness. They recognize the importance of continuous learning and improvement in today's rapidly changing business environment. Here are some key principles of organizational development:
Systemic Perspective
OD views organizations as complex systems made up of interrelated parts rather than a collection of individuals. This perspective recognizes that changes in one part of the organization can affect the entire system.
Participative Approach
OD involves active participation and collaboration from all members of the organization, including leaders, managers, employees and stakeholders. This approach values diversity of perspectives and promotes inclusion.
Continuous Improvement
Organizational development is an ongoing process of continuous learning, growth and improvement. This involves regularly assessing and evaluating the organization's performance and making adjustments as needed.
Human Focus
OD recognizes that organizations are made up of people, and therefore emphasizes the importance of understanding and supporting the human aspects of the organization, such as employee engagement, motivation and well-being.
Data-Driven Decision Making
Organizational development uses data and evidence to inform decision making and measure the impact of interventions. This involves collecting and analyzing data on organizational performance, employee feedback and other relevant metrics.
Collaborative Problem Solving
OD encourages collaborative problem solving and decision making. This involves bringing together diverse perspectives and expertise to address complex challenges and find innovative solutions.
Systems Thinking
Organizational development recognizes that organizations are part of larger systems, such as the economy, society and the environment. This involves considering the broader impact of organizational decisions and actions and seeking to create sustainable and responsible organizations.
The 5 Stages of Organizational Development
The stages of organizational development can vary depending on the model used, and it's important to note that these stages may not occur in a linear fashion. Organizations may revisit earlier stages as they continue to evolve and grow. Here are some commonly recognized stages:
Stage 1: Entry
The first phase is to enter and diagnose the current state of the organization. This involves identifying the strengths, weaknesses, opportunities and threats of the organization. The diagnosis can be done through surveys, interviews, focus groups and other methods of data collection.
Stage 2: Diagnosis
The second phase is to develop a plan for change based on the diagnosis. This includes setting goals, identifying areas for improvement and selecting appropriate interventions. The plan should be developed collaboratively with key stakeholders in the organization.
Stage 3: Feedback
The third phase is to implement the interventions identified in the planning phase. This will include providing feedback and may also include training, coaching, process redesign, culture change, etc. It is important to involve employees in the implementation process to ensure buy-in and ownership of the changes.
Stage 4: Solution
The fourth phase is to correct the concerns, close the gaps, improve the process and performance and then evaluate the effectiveness of the interventions. This involves measuring the impact of the changes on the organization and its stakeholders. The evaluation should be conducted using both qualitative and quantitative methods and should be ongoing to ensure continuous improvement.
Stage 5: Evaluation
The fifth and final phase is to institutionalize the changes into the organization's culture and processes. This involves embedding the changes into the organization's systems and structures to ensure they are sustainable and become part of the organization's way of doing things. Once implemented, collect data to analyze the effectiveness of the strategies implemented to understand if you are meeting your defined success indicators.

Organizational Development Techniques and Tools
OD techniques and tools improve the effectiveness and efficiency of an organization. There are several techniques and tools that can be used in organizational development. Some of these include:
SWOT Analysis
SWOT (strengths, weaknesses, opportunities, and threats) analysis is a tool that helps organizations identify their internal strengths and weaknesses and external opportunities and threats.
Change Management
Change management is the process of managing organizational change. It involves planning, implementing and monitoring changes to ensure that they are effective.
Team Building
Team building is the process of creating a cohesive team that works together effectively. This can involve team-building activities, training and development.
Process Improvement
Process improvement involves identifying and eliminating inefficiencies in organizational processes to improve efficiency and productivity.
Performance Management
Performance management is the process of setting goals, monitoring progress and providing feedback to employees to improve their performance.
Coaching and Mentoring
Coaching and mentoring are techniques used to develop the skills and knowledge of employees. This can involve one-on-one coaching or group mentoring sessions.
Employee Engagement
Employee engagement involves creating a work environment that fosters employee motivation, commitment and productivity.
Strategic Planning
Strategic planning is the process of defining an organization's goals and objectives and developing a plan to achieve them.
Employee Surveys
Employee surveys are used to gather feedback from employees on various aspects of the organization, such as job satisfaction, communication and leadership.
Training and Development
Training and development programs are used to develop the skills and knowledge of employees. This can include on-the-job training, workshops and seminars.
Topics

Katie Potter, MAIOP
Katie is an executive People & Talent leader with strong demonstration of building and scaling HR teams from startups to corporate teams. She has experience in building strong, globally focused culture & inclusion across remote, hybrid and onsite teams with a strong passion for people, engagement, & talent development.
Frequently asked questions
Other Related Terms
Eddy's HR Newsletter
Sign up for our email newsletter for helpful HR advice and ideas.