Eddy’s HR Mavericks Encyclopedia
The world's largest free encyclopedia of HR, with 700+ HR articles and podcasts.
Created by Eddy and our HR Mavericks community.
HR for Enterprise Businesses
Are you wondering if your organization needs HR? Do you think you will be successful without implementing an HR team? Maybe. But eliminating the risk and hiring HR professionals to lead the way for your people will result in much greater success for your organization. Read on to understand the importance of human resources in business and the key areas of operations that your human resources team should be responsible for.
What Is HR for Enterprise Businesses?
First, let's define human resources in general. HR can best be described as the division of a business that is tasked with finding, screening, recruiting, training, and supporting the people of the organization. To take this a step further, however, human resources is also responsible for partnering with key stakeholders throughout the organization to build culture strategy, conduct workforce planning, create policy and procedures, analyze compensation and benefits, mitigate risk and maintain compliance for the organization, as well as to recruit, hire, and train the workforce. In this article, we'll consider how HR works in a specific kind of organization: the enterprise business.
What Is an Enterprise Business?
An enterprise business is an organization founded and operated by an entrepreneur. The word enterprise is generally utilized to describe a “for-profit” business. Enterprise businesses are typically larger scale businesses that have been created to “meet a need” versus traditional businesses which are created to “make a profit.” Enterprise organizations are legal entities that possess the rights to conduct business on their own. This means they can enter into contracts, own property, incur liabilities and establish bank accounts. Enterprise businesses are typically (larger) corporations engaged in commercial, industrial or professional activities. They typically include a complex network of operations, departments, and divisions.
Why Is HR Important for Enterprise Businesses?
One of the most critical areas an organization can invest in is human resources. An HR team gives your organization a competitive edge. There are a myriad of reasons why having a human resource team for your organization is important; let's look at a few of them.
- HR improves company culture. Through thoughtful analysis and collaboration with company leadership, HR builds a culture strategy for the organization and ensures alignment across all other departments and teams.
- HR ensures better hires. Strategic workforce planning and candidate selection ensures that new hires are aligned to the company culture and can bring additional positive attributes to it.
- HR reduces turnover. Providing stronger candidate alignment/hires into the organization in conjunction with strong onboarding and ongoing training and development reduces turnover of employees.
- HR implements learning and development. Through ongoing training and learning and development initiatives, HR implements tools and resources that enable your workforce to continue growing professionally. Enhancing their skills results in increased performance, productivity, and retention.
- HR improves performance. Through creation of performance management policies and frameworks, your HR team can assist individuals who may fall short of meeting the requirements of their position. HR can also implement incentives to ensure performance across your workforce is strong enough to meet and exceed company goals.
- HR mitigates risk. HR analyzes statistical risk utilizing company data, prevents and addresses potential lawsuits, supervises termination practices, and works to protect the organization’s assets. HR leaders are (should be) well versed in business and employment law, ethics, statistics, strategy, and problem-solving in order to protect their company and its employees.
- HR provides meaningful engagement and connections. Thoughtful engagement activities and connection-building across your workforce strengthens collaboration and teamwork and ensures a cohesive and positive approach towards these items as the workforce drives towards company goals.
- HR helps workers adjust to work and changes, decreasing loss of productivity. From efficient and effective onboarding to training and development practices, an HR team assesses skill gaps across your workforce and proactively implements training initiatives to prevent loss of productivity. Additionally, HR implements positive change-management training and communications across your organization to help workers understand and adjust to necessary changes.
Roles of HR for Enterprise Businesses
The role of HR in enterprise businesses is multifaceted and has a direct impact on the company’s success through its most important asset: its people. HR leads the departments within the organization that directly impact employees with a focus on efficiency, support, and staff well-being.
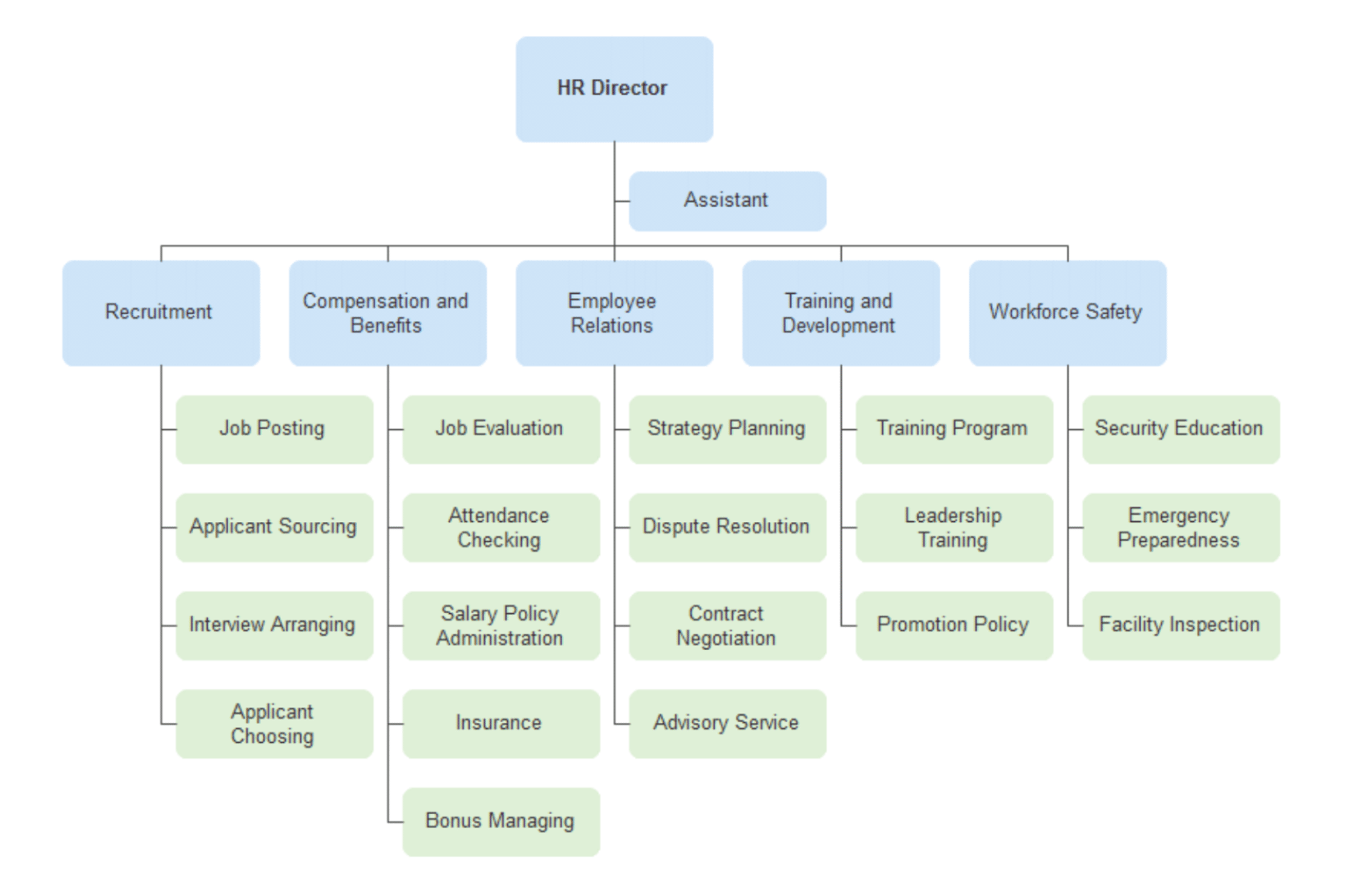
Culture Strategy
Workplace culture is best described as a combination of all the parts of our work—behaviors, values and systems—that create an experience for employees and customers. Culture strategy is a clear set of priorities that equip leaders to drive people-centered outcomes. It involves creating a plan that determines how things get done within the workplace while being mindful of the way in which operations, beliefs, and company values impact employees and their behaviors, performance and experience. HR works directly with the CEO and leadership team to strategize, define, and execute the culture strategy for the organization.
Recruitment and Hiring
Recruiting and hiring sources, attracts, vets, interviews and hires talent into the organization. The recruitment function is tasked with understanding hiring needs, preparing job descriptions, planning a recruitment strategy in line with workforce planning and hiring needs, and sourcing, screening and shortlisting candidates. It brings candidates through the full recruitment process, extending offers of employment and onboarding new talent into the company. The interview process itself has a multitude of nuances depending on the position, job description, and hiring manager's needs.
Training & Development
The training and development function is responsible for improving the productivity of employees with a focus on building and enhancing professional skills. This function creates, plans and executes training initiatives that address key areas of development, skill gaps, or particular skillsets needed throughout the organization. This function oversees the development of employees to ensure that company goals can be met. Reviewing the training budget and costs associated with any third-party learning is also a part of this function.
Employee Relations
Employee relations is an HR function that builds positive working relationships and interactions across employers and employees. ER provides direction, oversight and guidance for employee-related matters, including time off, leaves of absence, formal and informal employee complaints, investigation of harassment and discrimination claims, termination of employees, and unemployment compensation claims. At times, employee relations work coordinates educational opportunities. ER works to develop policies, interpret policies and collective bargaining agreements, facilitate public relations, and mediate conflicts.
Compensation and Benefits
Creating a compensation and benefits model is integral to attracting talent, enhancing engagement and retaining your employees. HR strives to ensure that the compensation and benefits model being utilized is fair, equitable and without discrimination. HR works to evaluate and analyze benefit vendors to ensure that budgets are being met and employees are being supported through benefits offerings. Creating a compensation structure that is competitive to the market and industry is also a focus in this sector of HR. HR team members in this space oversee payroll, including state and federal compliance.
Employment Law, Risk Management and Compliance
HR takes a proactive approach to identify employee-related risks before they happen. In various situations, such as poor/ineffective leadership or inappropriate employee behavior, HR proactively assesses and analyzes outcomes before these risks appear. Preparing for potential employee-related risks across the organization and effectively handling these situations is a critical piece of human resources. HR establishes protocol so that when issues do arise, there is a de-escalation plan in place. Satisfied employees are much less likely to have these types of concerns, which makes the other functions of HR that much more important. In addition to risk management, HR is responsible for ensuring compliance across all people-related functions within the organization, including policies, procedures, payroll, benefits administration, and more.
Employee Safety
It is the responsibility of HR to ensure that the organization invests in a proactive safety culture. A key element of this is providing effective training and development for employees. In this function, HR creates, administers and implements the company’s safety culture, which includes the overall company culture, company policies and procedures, proper monitoring and updating of any safety plan the company has in place, and compliance to federal and state regulations. HR champions safety across the organization and leads the implementation of safe work initiatives.
Company Policy and Procedure
HR works to ensure that all company policies and procedures are aligned and meet all legal and compliance requirements. HR ensures transparency and easy access to all policies and procedures across the organization. This will be the area (usually found within an employee intranet) where HR communicates the company's mission, values, and goals, as well as the context for various company programs, such as orientation, onboarding, and employee training. HR is responsible for the creation, execution and iteration of all policies and procedures affecting employees.
Challenges of HR for Enterprise Businesses
HR faces many challenges, some of which are persistent, ongoing, and require strategic thought and planning to adequately address. While not a full list of all challenges that can be presented under the HR realm of responsibility, below is a list of the most common.
Employee Engagement
Seventy-one percent of executives agree that employee engagement is an essential factor in an organization’s success. Engagement impacts everything from retaining your employees right down to your bottom line and overall profitability. The concern for HR is that chronic disengagement remains an issue for many organizations. This issue has been exacerbated by remote work.
Recruiting, Onboarding and Retention
The talent function within HR supports attracting, engaging, and hiring new talent into the organization. Aligning candidates with the right skills and culture fit can be a challenge. Working to successfully onboard and keep employees engaged throughout the full employee lifecycle also presents a challenge. HR must ensure that these pieces of the recruitment and engagement function are successful, supplying each employee with all of the tools, resources, and support they need to have a fulfilling career within your organization.
Employee Health and Well Being
HR keeps a consistent focus on employee wellness. As physical and emotional wellbeing declines, so does productivity and performance. Employee wellness issues will always be present. A 2020 Gallup report reported that 76% of employees experience burnout at least sometimes.
Diversity, Equity, and Inclusion
The key to a healthy organization that attracts the best talent is strong practice and focus on diversity, equity and inclusion. Glassdoor reported that in 2020, 76% of employees valued a diverse workforce. The challenge for HR is to consistently keep all three goals at the forefront along with ensuring that they are building a true culture of belonging for all employees.
Supporting Leadership
It is the responsibility of HR to ensure that leaders across the organization have the tools, knowledge, resources, and constant support they need to succeed and fully support their teams. HR provides mentorship and coaching to leaders to create a culture of positive collaboration and support. Training leaders to be effective listeners and influential people managers is a challenge, as leadership styles vary greatly. Working to align different leadership styles with company culture and values can be difficult.
Adapting to Remote Work
Remote work is here to stay. It may not be a fit for all organizations, but employees across many organizations have a preference for remote work. According to FlexJobs, 65% of respondents to their Career Pulse Survey (conducted between July and August 2022) indicated a preference for working fully remotely, while 32% had a preference for hybrid work and 3% wished to return full time to the office. That is an astounding 97% of employees who preferred to maintain some form of remote work. Remote work presents challenges, as HR needs to provide additional training, tools and technology to ensure effective communication, collaboration and connectedness. Positively supporting and keeping employees engaged while working remotely may also present challenges.
Building a Winning Culture
Kellie Wong, Senior Content Marketing Manager at Achievers, defines organizational culture as “...the values, expectations, and practices that guide and inform the team members’ daily actions.” A winning culture includes positive traits that promote performance, such as employee recognition, employee voice, company values, belonging and effective leadership. Building a winning culture can be a challenge if all of these pieces are not in alignment and at the forefront of the work being done across the entire organization.
Topics

Katie Potter, MAIOP
Katie is an executive People & Talent leader with strong demonstration of building and scaling HR teams from startups to corporate teams. She has experience in building strong, globally focused culture & inclusion across remote, hybrid and onsite teams with a strong passion for people, engagement, & talent development.
Frequently asked questions
Other Related Terms
Eddy’s HR Mavericks Encyclopedia
HR for Enterprise Businesses
Are you wondering if your organization needs HR? Do you think you will be successful without implementing an HR team? Maybe. But eliminating the risk and hiring HR professionals to lead the way for your people will result in much greater success for your organization. Read on to understand the importance of human resources in business and the key areas of operations that your human resources team should be responsible for.
What Is HR for Enterprise Businesses?
First, let's define human resources in general. HR can best be described as the division of a business that is tasked with finding, screening, recruiting, training, and supporting the people of the organization. To take this a step further, however, human resources is also responsible for partnering with key stakeholders throughout the organization to build culture strategy, conduct workforce planning, create policy and procedures, analyze compensation and benefits, mitigate risk and maintain compliance for the organization, as well as to recruit, hire, and train the workforce. In this article, we'll consider how HR works in a specific kind of organization: the enterprise business.
What Is an Enterprise Business?
An enterprise business is an organization founded and operated by an entrepreneur. The word enterprise is generally utilized to describe a “for-profit” business. Enterprise businesses are typically larger scale businesses that have been created to “meet a need” versus traditional businesses which are created to “make a profit.” Enterprise organizations are legal entities that possess the rights to conduct business on their own. This means they can enter into contracts, own property, incur liabilities and establish bank accounts. Enterprise businesses are typically (larger) corporations engaged in commercial, industrial or professional activities. They typically include a complex network of operations, departments, and divisions.
Why Is HR Important for Enterprise Businesses?
One of the most critical areas an organization can invest in is human resources. An HR team gives your organization a competitive edge. There are a myriad of reasons why having a human resource team for your organization is important; let's look at a few of them.
- HR improves company culture. Through thoughtful analysis and collaboration with company leadership, HR builds a culture strategy for the organization and ensures alignment across all other departments and teams.
- HR ensures better hires. Strategic workforce planning and candidate selection ensures that new hires are aligned to the company culture and can bring additional positive attributes to it.
- HR reduces turnover. Providing stronger candidate alignment/hires into the organization in conjunction with strong onboarding and ongoing training and development reduces turnover of employees.
- HR implements learning and development. Through ongoing training and learning and development initiatives, HR implements tools and resources that enable your workforce to continue growing professionally. Enhancing their skills results in increased performance, productivity, and retention.
- HR improves performance. Through creation of performance management policies and frameworks, your HR team can assist individuals who may fall short of meeting the requirements of their position. HR can also implement incentives to ensure performance across your workforce is strong enough to meet and exceed company goals.
- HR mitigates risk. HR analyzes statistical risk utilizing company data, prevents and addresses potential lawsuits, supervises termination practices, and works to protect the organization’s assets. HR leaders are (should be) well versed in business and employment law, ethics, statistics, strategy, and problem-solving in order to protect their company and its employees.
- HR provides meaningful engagement and connections. Thoughtful engagement activities and connection-building across your workforce strengthens collaboration and teamwork and ensures a cohesive and positive approach towards these items as the workforce drives towards company goals.
- HR helps workers adjust to work and changes, decreasing loss of productivity. From efficient and effective onboarding to training and development practices, an HR team assesses skill gaps across your workforce and proactively implements training initiatives to prevent loss of productivity. Additionally, HR implements positive change-management training and communications across your organization to help workers understand and adjust to necessary changes.
Roles of HR for Enterprise Businesses
The role of HR in enterprise businesses is multifaceted and has a direct impact on the company’s success through its most important asset: its people. HR leads the departments within the organization that directly impact employees with a focus on efficiency, support, and staff well-being.

Culture Strategy
Workplace culture is best described as a combination of all the parts of our work—behaviors, values and systems—that create an experience for employees and customers. Culture strategy is a clear set of priorities that equip leaders to drive people-centered outcomes. It involves creating a plan that determines how things get done within the workplace while being mindful of the way in which operations, beliefs, and company values impact employees and their behaviors, performance and experience. HR works directly with the CEO and leadership team to strategize, define, and execute the culture strategy for the organization.
Recruitment and Hiring
Recruiting and hiring sources, attracts, vets, interviews and hires talent into the organization. The recruitment function is tasked with understanding hiring needs, preparing job descriptions, planning a recruitment strategy in line with workforce planning and hiring needs, and sourcing, screening and shortlisting candidates. It brings candidates through the full recruitment process, extending offers of employment and onboarding new talent into the company. The interview process itself has a multitude of nuances depending on the position, job description, and hiring manager's needs.
Training & Development
The training and development function is responsible for improving the productivity of employees with a focus on building and enhancing professional skills. This function creates, plans and executes training initiatives that address key areas of development, skill gaps, or particular skillsets needed throughout the organization. This function oversees the development of employees to ensure that company goals can be met. Reviewing the training budget and costs associated with any third-party learning is also a part of this function.
Employee Relations
Employee relations is an HR function that builds positive working relationships and interactions across employers and employees. ER provides direction, oversight and guidance for employee-related matters, including time off, leaves of absence, formal and informal employee complaints, investigation of harassment and discrimination claims, termination of employees, and unemployment compensation claims. At times, employee relations work coordinates educational opportunities. ER works to develop policies, interpret policies and collective bargaining agreements, facilitate public relations, and mediate conflicts.
Compensation and Benefits
Creating a compensation and benefits model is integral to attracting talent, enhancing engagement and retaining your employees. HR strives to ensure that the compensation and benefits model being utilized is fair, equitable and without discrimination. HR works to evaluate and analyze benefit vendors to ensure that budgets are being met and employees are being supported through benefits offerings. Creating a compensation structure that is competitive to the market and industry is also a focus in this sector of HR. HR team members in this space oversee payroll, including state and federal compliance.
Employment Law, Risk Management and Compliance
HR takes a proactive approach to identify employee-related risks before they happen. In various situations, such as poor/ineffective leadership or inappropriate employee behavior, HR proactively assesses and analyzes outcomes before these risks appear. Preparing for potential employee-related risks across the organization and effectively handling these situations is a critical piece of human resources. HR establishes protocol so that when issues do arise, there is a de-escalation plan in place. Satisfied employees are much less likely to have these types of concerns, which makes the other functions of HR that much more important. In addition to risk management, HR is responsible for ensuring compliance across all people-related functions within the organization, including policies, procedures, payroll, benefits administration, and more.
Employee Safety
It is the responsibility of HR to ensure that the organization invests in a proactive safety culture. A key element of this is providing effective training and development for employees. In this function, HR creates, administers and implements the company’s safety culture, which includes the overall company culture, company policies and procedures, proper monitoring and updating of any safety plan the company has in place, and compliance to federal and state regulations. HR champions safety across the organization and leads the implementation of safe work initiatives.
Company Policy and Procedure
HR works to ensure that all company policies and procedures are aligned and meet all legal and compliance requirements. HR ensures transparency and easy access to all policies and procedures across the organization. This will be the area (usually found within an employee intranet) where HR communicates the company's mission, values, and goals, as well as the context for various company programs, such as orientation, onboarding, and employee training. HR is responsible for the creation, execution and iteration of all policies and procedures affecting employees.
Challenges of HR for Enterprise Businesses
HR faces many challenges, some of which are persistent, ongoing, and require strategic thought and planning to adequately address. While not a full list of all challenges that can be presented under the HR realm of responsibility, below is a list of the most common.
Employee Engagement
Seventy-one percent of executives agree that employee engagement is an essential factor in an organization’s success. Engagement impacts everything from retaining your employees right down to your bottom line and overall profitability. The concern for HR is that chronic disengagement remains an issue for many organizations. This issue has been exacerbated by remote work.
Recruiting, Onboarding and Retention
The talent function within HR supports attracting, engaging, and hiring new talent into the organization. Aligning candidates with the right skills and culture fit can be a challenge. Working to successfully onboard and keep employees engaged throughout the full employee lifecycle also presents a challenge. HR must ensure that these pieces of the recruitment and engagement function are successful, supplying each employee with all of the tools, resources, and support they need to have a fulfilling career within your organization.
Employee Health and Well Being
HR keeps a consistent focus on employee wellness. As physical and emotional wellbeing declines, so does productivity and performance. Employee wellness issues will always be present. A 2020 Gallup report reported that 76% of employees experience burnout at least sometimes.
Diversity, Equity, and Inclusion
The key to a healthy organization that attracts the best talent is strong practice and focus on diversity, equity and inclusion. Glassdoor reported that in 2020, 76% of employees valued a diverse workforce. The challenge for HR is to consistently keep all three goals at the forefront along with ensuring that they are building a true culture of belonging for all employees.
Supporting Leadership
It is the responsibility of HR to ensure that leaders across the organization have the tools, knowledge, resources, and constant support they need to succeed and fully support their teams. HR provides mentorship and coaching to leaders to create a culture of positive collaboration and support. Training leaders to be effective listeners and influential people managers is a challenge, as leadership styles vary greatly. Working to align different leadership styles with company culture and values can be difficult.
Adapting to Remote Work
Remote work is here to stay. It may not be a fit for all organizations, but employees across many organizations have a preference for remote work. According to FlexJobs, 65% of respondents to their Career Pulse Survey (conducted between July and August 2022) indicated a preference for working fully remotely, while 32% had a preference for hybrid work and 3% wished to return full time to the office. That is an astounding 97% of employees who preferred to maintain some form of remote work. Remote work presents challenges, as HR needs to provide additional training, tools and technology to ensure effective communication, collaboration and connectedness. Positively supporting and keeping employees engaged while working remotely may also present challenges.
Building a Winning Culture
Kellie Wong, Senior Content Marketing Manager at Achievers, defines organizational culture as “...the values, expectations, and practices that guide and inform the team members’ daily actions.” A winning culture includes positive traits that promote performance, such as employee recognition, employee voice, company values, belonging and effective leadership. Building a winning culture can be a challenge if all of these pieces are not in alignment and at the forefront of the work being done across the entire organization.
Topics

Katie Potter, MAIOP
Katie is an executive People & Talent leader with strong demonstration of building and scaling HR teams from startups to corporate teams. She has experience in building strong, globally focused culture & inclusion across remote, hybrid and onsite teams with a strong passion for people, engagement, & talent development.
Frequently asked questions
Other Related Terms
Eddy's HR Newsletter
Sign up for our email newsletter for helpful HR advice and ideas.